
- Home
- ESTIMATING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF INFECTIOUS PROPAGULES (IP) USING MPN METHOD

Aditi Bijalwan
Co-founder at Agrilogy Bioscience Private Limited
Estimating the concentration of viable mycorrhizal propagules in a sample is a crucial step in assessing the effectiveness of biofertilizers and soil inoculants. In this post, we break down the step-by-step process of calculating the Most Probable Number (MPN) of infective propagules using dilution series and replicate tube assays—making a complex method simple and approachable for researchers, students, and industry professionals alike.
What is the MPN Method?
The Most Probable Number (MPN) method is a statistical technique used to estimate the number of viable microorganisms—such as infective propagules (IP) of mycorrhizal fungi—in a given sample. It relies on a series of dilutions and observations of microbial growth (or colonization) in multiple replicates to calculate a probable concentration in the original sample.
Experimental Setup
In this case, four serial dilutions of a sample (10⁻¹, 10⁻², 10⁻³, and 10⁻⁴) were tested. Each dilution was replicated in 5 tubes to observe mycorrhizal colonization. The number of tubes showing positive colonization at each dilution was recorded as follows:
- 10⁻¹: 5/5 tubes positive
- 10⁻²: 5/5 tubes positive
- 10⁻³: 3/5 tubes positive
- 10⁻⁴: 2/5 tubes positive
Identifying the MPN Index
To calculate the MPN, you only need the results from the last three consecutive dilutions that show a decreasing number of positive tubes:
- P1 = 5 (from 10⁻² dilution)
- P2 = 3 (from 10⁻³ dilution)
- P3 = 2 (from 10⁻⁴ dilution)
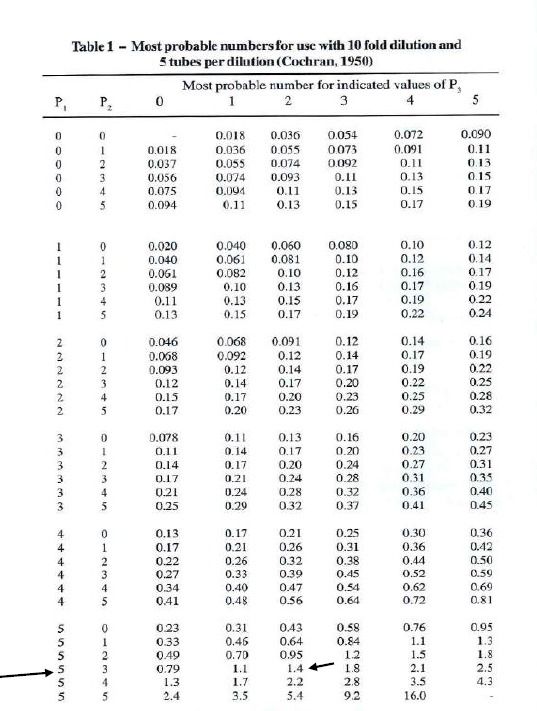
This gives an MPN index of 5-3-2.
Using the MPN Table
Next, consult a standard 5-tube MPN table to find the most probable number corresponding to the 5-3-2 combination. According to the MPN table, the value is:
➡️ 14
This number represents the most probable number of infective propagules in the dilution level of P2.
Calculating Total IP/g of Substrate
Now, use the following formula to calculate the total number of infective propagules per gram of substrate:
Total IP/g=MPN value×Dilution factor of P2/Dry mass of sample (g)
Given:
- MPN value = 14
- Dilution factor of P2 (10⁻³) = 1000
- Dry mass of product sample = 10 g
Total IP/g=14×1000/10=1400 IP/g
Conclusion
The MPN method provides a statistically sound and practical way to estimate infective propagules in soil or inoculant samples. In this example, the sample contains 1400 infective propagules per gram—a critical metric for evaluating biofertilizer quality and microbial inoculant potency.
Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!




Leave a Comment